The main task in the development of public control is to increase the transparency of the decision-making process by officials, strengthen feedback between state and municipal authorities and the population, and, as a result, increase the level of public credibility in the state in general. This work has been substantially built up in several directions: work with citizens' petitions, activization of regional civic chambers and public councils, methodological assistance of PMCs, and public expertise of the most important legislative initiatives.
#Citizens’ petititions as a tool to understand the "people’s agenda"
In 2019 (as of December 1, 2019), the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation received 17,042 citizens’ petititions. The source of petititions is via both the Russian Post and other channels: through the personal reception of citizens in the Chamber's building, via a special form for electronic petititions on the Chamber’s website – oprf.ru, and through the hotline (call center).
The Central Federal District (CFD) remains the leader in the number of petititions. In absolute terms, 6,636 requests were received from this district. The Far Eastern Federal District is where the least number of petititions come from.
The number of petititions received by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, in terms of federal districts
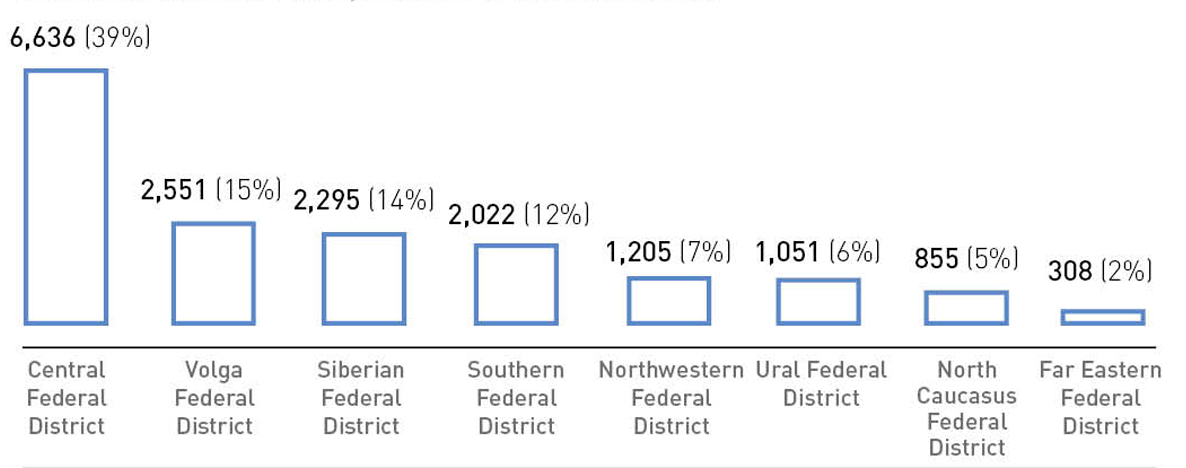
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation
The number of petititions received by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation in terms of federal districts (relative population of districts), per 100,000
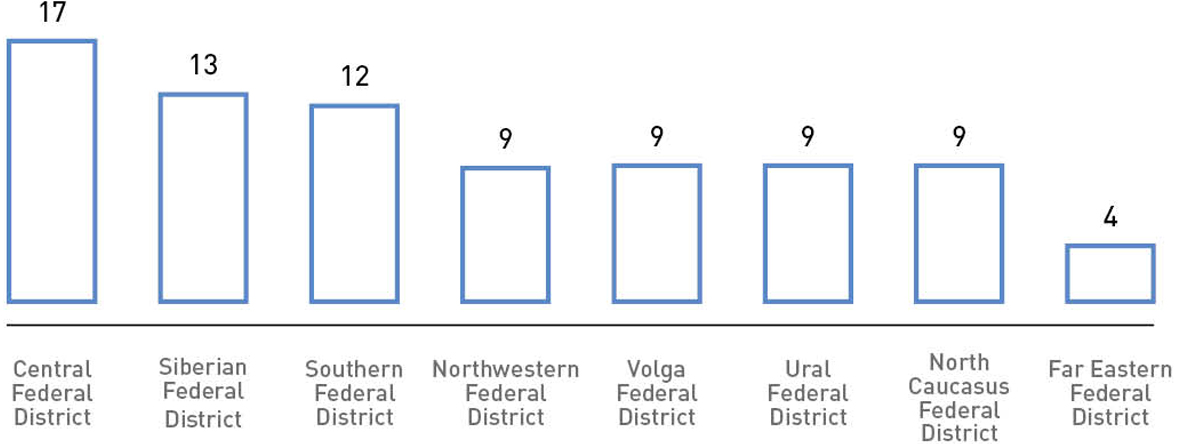
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation
The main portion of petititions concerns the judicial and law enforcement system, social sphere, and housing and communal services. Matters of housing and communal services are traditionally the most frequently topic come across in citizens' petititions. Hundreds of petititions are sent annually to the state authorities in constituent entities, local self-governments, and supervisory and control organizations.
As a whole a series of cases have achieved results.
For example, in March, the Civic Chamber received a collective petition signed by more than 4,500 residents of the city of Pokrov and the Petushinsky district in the Vladimir Region, who were protesting against a project to build a section of the Moscow-Kazan high-speed railway through a residential development of the city of Pokrov.
The results of the audit carried out by members of the Chamber were sent to the President of the Russian Federation V.V. Putin with a request to give an order to construct the route of the highway without affecting the existing populated areas. At present a decision has been taken to halt the highway's construction.7
Topics of citizens' appeals received by the Civic Chamber of Russia, %
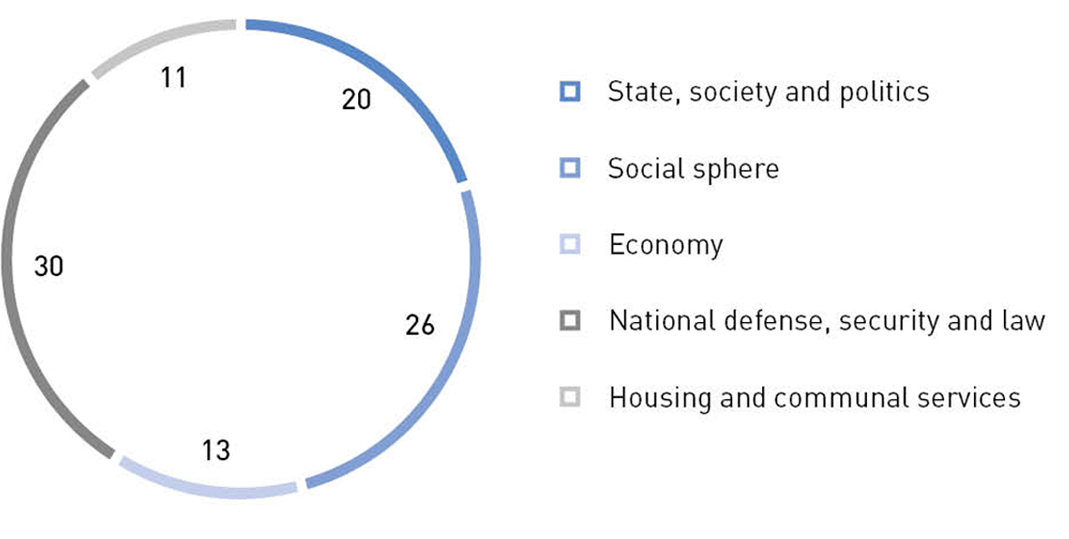
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation

Another collective petition from the city of Pokrov, contained a protest against a capital repair of the Volga federal highway M-7 within the city. According to the capital repair project, the road passing through the city and its historic center has been upgraded to a highway and practically divides the city into two isolated sections. Based on the results of a field meeting held in the city of Pokrov, and a meeting that followed at Rosavtodor, the possibility of rejecting the project's implementation until a mutually acceptable solution has been reached is under consideration.8
Members of the Civic Chamber often have to deal with the level of competence and the negligence of local self-governments functionaries. For example, a citizen living in the city of Kovrov, Vladimir Region, turned to the Civic Chamber hotline on issues related to the activities of medical and social examination institutions. The MSA bureau requested control documents for his case at the behest of the Chamber. After that, the local MSA suddenly revised its own decision and changed the disability group from second to first. In another case, an airline ordered a single mother of two disabled children to buy 13 tickets to transport them after an operation from the city of Kurgan back home via a flight through Moscow.
An inspection conducted at the request of a member of the Civic Chamber, Diana Gurtskaya, resulted in two administrative cases against the airline under two articles: “Sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services in the absence of established information” and “Deception of consumers” of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation.
For several months, members of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation dealt with a problem in the city of Kostomuksha in the Republic of Karelia, where, based on a lawsuit by the city administration, a court decided to limit the parental rights of a family with multiple children; six children were taken away from their parents. The suit against the family included inadequate living conditions, lack of sleeping and working places for lessons, etc., while the necessary conditions for living and educating children in the family were created. After an address by the Chamber to the governor of Karelia, the situation became highly publicized. In May 2019, the court quashed the restriction and immediately returned the children back home.
Working with citizens' petititions is a high priority and will continue. New formats are being developed. The practice of having a "zero day" before each "Community" forum has proven itself - members of the Chamber, arriving for the forum, conduct excursions according to citizens' petititions from that region, helping to resolve local issues. Methodological work with regional chambers to organize work with citizens' petititions is being conducted.

#Regional civic chambers as public-state dialog sites
In regions civic chambers are first and foremost sites for public dialog. According to Federal Law No. 183-FZ from June 23, 2016 “On General Principles of Organization and Activity of Civic Chambers of the Constituent Entities of the Russian Federation”9 and the relevant laws of the constituent entities, civic chambers were created in all regions of Russia to protect the rights and freedoms, to concern the needs and interests of citizens and non-profit organizations in the formation and implementation of state policy, and to ensure public supervision of authorities' activities.

The total number of members of regional civic chambers exceeds 3,500. The activities of most chambers are organized within the framework of relevant commissions. To date, 83 civic chambers in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have 646 commissions acting in various areas. As a rule, the main commissions deal with social issues, e.g. healthcare, education, housing and public utilities, demography, public control, etc. The name of the commissions reflects regional specifics. For example, the Civic Chamber of Moscow has a commission on “Smart City” technology. The civic chambers of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous District – Yugra, the Yamal-Nenets Autonomous District and the Krasnoyarsk Territory, have commissions that deal with matters of the indigenous peoples of the North.10
Civic chambers cooperate with the full range of non-profit organizations – veteran, youth, trade unions, educational and environmental, societies for the protection of historical and cultural monuments, but analysis shows that non-official civic initiatives still lack proper support. According to a Civic Chamber survey during the “Community” forum11 , the number of NPO employees and civil society activists engaged in the work of civic chambers is growing annually, but up to half of the representatives of the third sector do not participate in their activities. Hence, we need to improve feedback channels and support mechanisms here.
Have you personally participated in the activities of a regional Civic Chamber?
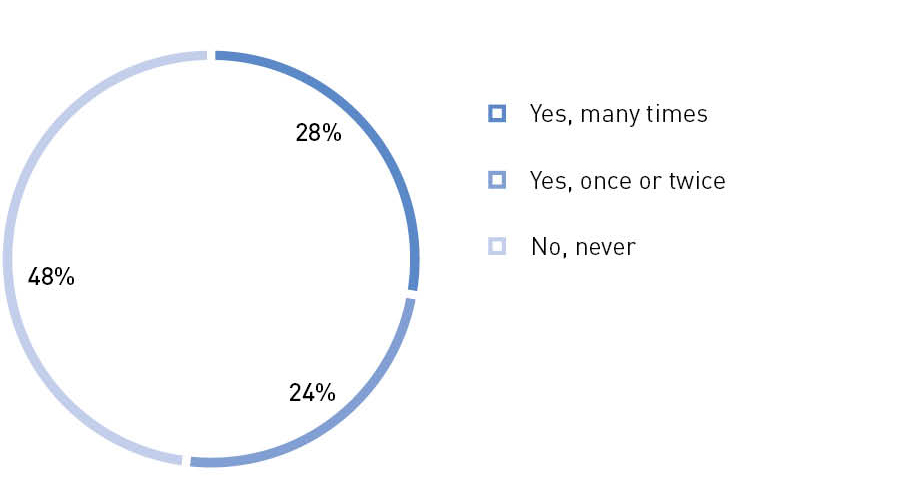
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation12
How do you evaluate your experience in communicating with a regional Civic Chamber?
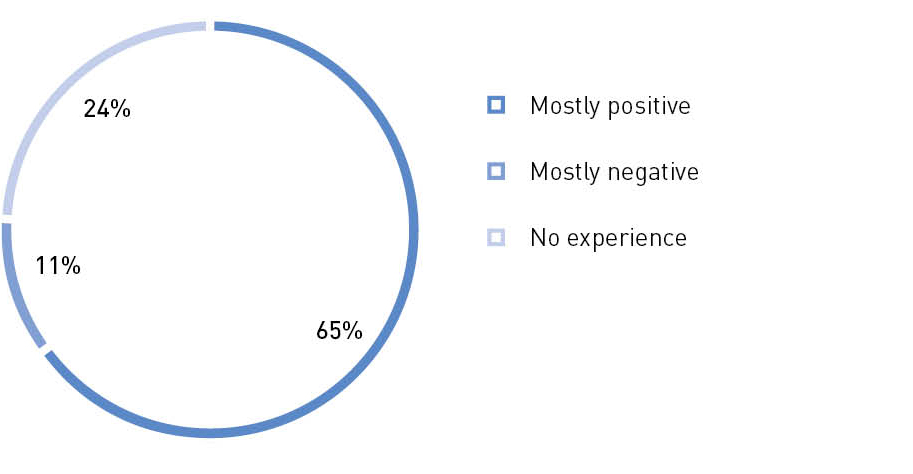
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation 13
Approximately half of the survey’s respondents during the “Community” forum believe that the civic chamber of their region acts as a platform for interaction between the non-profit sector, civil society activists, business, and government. The other half of the respondents believe that the chamber is not a successful platform for interaction, or they do not have a definite answer to this question. In general, the potential for regional civic chambers as institutions to organize civil society at the local level is quite high. At the same time, the goal for both the Federal Chamber and regional chambers should be an assessment of their work, when the absolute majority of respondents recognize the chambers' active influence on the dynamics of public opinion and the promotion of public initiatives.
Against this backdrop, it is disappointing to see the situation in Sevastopol, where the civic chamber did not hold a single meeting in 2019 due to the lack of a quorum. This raises the question about the need to form a new composition of the chamber after the dissolution of the current composition, however, such a mechanism is not provided for by law, and the rules of the chamber have not been adopted.14
Meanwhile, an increase in the activity of regional chambers is indicated by monitoring data on the openness and transparency of their websites.15 The most common format for reporting on the activities of civic chambers is the news: all 83 websites have this section. Announcements about upcoming events are published by 48 websites of regional chambers. Thirty websites have a special section dedicated to the examination of bills, 18 websites have reports directed toward the authorities. Fifteen websites have texts of legal acts regulating the issues of working with citizens' petitions. None of these websites have information on the chamber's budget performance.
Based on the set of criteria (functionality, relevance, and interactivity), the monitoring leaders in 2019 remain the websites of the civic chambers in the Kirov, Yaroslavl, and Chelyabinsk Regions, as well as the Krasnodar Territory. In 2019, the website of the Civic Chamber of the Komi Republic was among the leaders.17
Do you think the Civic Chamber of your region carries out its functions as a platform for interaction between the non-profit sector, civil society activists, business, and government?
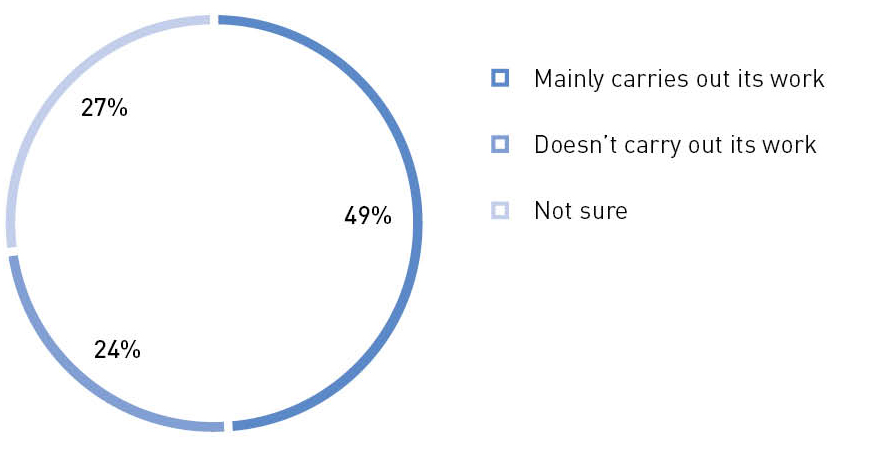
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation16
The civic chamber of any region as a platform for a dialog primarily depends on the position of the members themselves, but also on the resources available, and the attitude of regional governments: where the governments are more engaged in the discussion of current problems, the better the conditions for dialog and the search for acceptable solutions.
In this context, it is gratifying to see that in recent years the greatest achievements of the chambers are related to the development of public control. Back in 2018, the chambers were actively involved in the organization of public watchdogs in elections. The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, together with the CEC of Russia, developed a gold standard for observing the enforcement of citizens' electoral rights. And this standard was used by public watchdogs to assess the situation in specific polling stations. In 2018, more than 150,000 watchdogs across all regions of the country took part in public control of the presidential election. In 2019, the practice of public observation was continued and developed. The necessary amendments to legislation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation made it possible to attract almost 40,000 watchdogs to public control in regional elections. At the same time, working groups that monitored the election process in the most difficult regions in terms of possible violations were formed in close cooperation with the Presidential Council for Civil Society and Human Rights and non-governmental human rights organizations.
The second most important direction to enhance public control in 2018–2019 is the implementation of national projects and the achievement of targets of the presidential decree from May 7, 2018. Many regional civic chambers created working groups on public control of the implementation of national projects as part of this work. For example, the Civic Chamber of the Republic of Khakassia formed such a group, which in addition to members of the regional chamber, includes chairmen of municipal civic chambers and public councils under executive authorities. Following the studying of the passports of regional projects, “road maps” for public monitoring were compiled. The head of the republic and the heads of regional ministries took part in a plenary meeting of the republican Civic Chamber in September 2019.18 The Civic Chamber of the Volgograd Region implemented a working group to supervise the execution of the May Decrees; members of the Chamber are also members of the project committees involved in the implementation of national projects in the region.19
The Civic Chamber of the Vologda Region developed a system of public control for the national project “Safe and High-Quality Roads” to monitor the formation and use of road funds at all levels. Joint work with the Department of Public Road Administration and Transport of the Government of the Vologda Region resulted in a photo illustrated memo for public controllers.20 The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, together with colleagues from the regions, summarize best practices in this area and facilitate their spread.

The specific agenda of public control in the regions is diverse. However, as a rule, it focuses on people's everyday problems. For example, after the intervention of the St. Petersburg Civic Chamber, it was possible to help home buyers who asked public activists to monitor the construction of several residential complexes and verify the quality of the work being carried out at the facilities. Thanks to the Civic Chamber defrauded home buyers were able to sit down at the negotiating table for the first time and ask questions. Based on the consultations, participants in shared construction received assurances that it planned to complete the construction and put into operation 21 “problem” residential buildings. The Civic Chamber of the Republic of Tatarstan is also involved in resolving the problems of defrauded home buyers and performs public control of housing construction.21
The Ulyanovsk Region has a broad network of municipal councils on public control in the field of medicinal supply, road maintenance, the availability and condition of sports facilities, and the availability of medical and cultural facilities under the program "Accessible Environment". More than 2,500 people participate in the work of such councils. Launched in 2014, the practice of hearing reports by members of the Government of the Ulyanovsk Region on their activities and the activities of subordinate institutions successfully distinguished itself. Public activists have the opportunity to communicate directly with the heads of ministries; questions and topics for discussion are then referred to the authorities.
In the Sakhalin Region, regional and municipal civic chambers took part in the implementation of the project “Special Child’s Opportunities Map”. More than 1,500 people took part in a survey on health problems in the region. It helped to identify the main issues: staffing and health services accessibility (some services can be given only in medical institutions located in the central regions of Russia or abroad, which, in turn, leads to large and sometimes enormous financial costs).
In St. Petersburg, the attention of the Civic Chamber helped to speed up the process of combining social and medical services. Public activists have repeatedly reported about the need not only for one-time, but comprehensive and long-term assistance to citizens, especially the elderly. On July 1, the city opened a Social Service Center and a social neighborhood physician. The new structure keeps records of citizens who need various types of social and medical assistance. The St. Petersburg Civic Chamber also initiated amendments to the Law “On Grants of St. Petersburg for Public Associations”. Today, this new legislation allows public organizations to receive financial resources even prior to the start of a project. The proposals by the St. Petersburg Civic Chamber were also included in "The Plan for the Implementation of the Strategy of Action for Women" and in "Assistance to Elderly Citizens".22
The results of monitoring made by the Civic Chamber of Russia have shown that 10 regional civic chambers have been vested with the right to make legislative initiatives.23 The Civic Chamber of the Kaliningrad Region actively implements this opportunity. In particular, such an initiative helped Kaliningrad Region law No. 304 from July 1, 2019 “On Public Councils under the Government of the Kaliningrad Region” to be adopted.24 In 2019, the Civic Chamber of the Kursk Region prepared a regional bill “On Patrons and Patronage Activities”. This bill is included in the rule-making plan of the Kursk Regional Duma.25 The experience of granting the legislative initiative to the subjects of public control seems to be an important area for expert study at a platform of the Federal Civic Chamber and within the framework of the "Community" forum in 2020.
The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation is not the governing body for the regional chambers. While at the same time, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation does provide methodological support for regional civic chambers. Such support is aimed at consolidating the principles of self-government, independence, openness, and transparency in their everyday activities. Despite the representatives of all regional chambers having the opportunity to interact at plenary meetings of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, in order to ensure constant interregional interaction on public control, the Council of Civic Chambers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation coordinates the activities of regional chambers in terms of implementing new prioritized initiatives and interregional projects, and facilitates the interchange of experience and best practices. The monitoring conducted by the Council shows that regional civic chambers still have many organizational problems. Often such problems include the weak activity of the chambers, lack of competencies for establishing constructive interaction with the authorities, the media, NPOs, and organization of activities on public control. These problems can be solved with more coordination between the chambers for an intensive exchange of positive experiences.
As a response to this problem, in November 2019, members of regional civic chambers could attend a series of training seminars held as part of the project "The Civic Chamber's University". The module was attended by 49 leaders of public activists from different regions of the country, some of whom were selected at previous sessions of the Civic Chamber's University, the rest passed competitive selection. As part of the project, young leaders are taught to find resources through which social change can be launched in the regions.

Have you personally participated in municipal (city or district) civic chamber events where you reside?
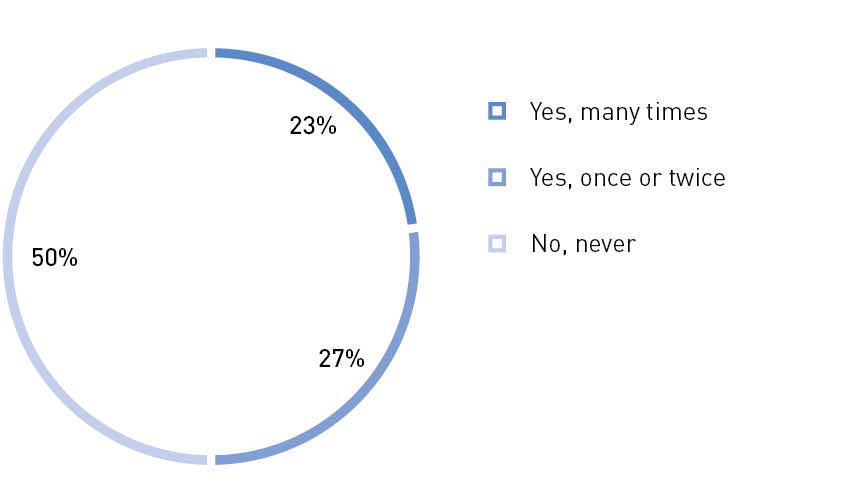
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation26
The experience of 2019 showed that in a number of socially significant conflict situations at the local level, the role of civic chambers as an organized institution of civic dialog was not quite in line with their potential. In the scheme of things, we can talk about the shortcomings of the mechanism to form civic chambers, which often make them dependent on the regional political situation. In light of this, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation is discussing legislative changes aimed at improving the mechanisms to form civic chambers.
As has been repeatedly highlighted, the implementation of the principles on which the chambers' activities shall be based is currently hindered by legislative gaps in establishing a minimum level of financial support for their activities. The issue of financial support often mitigates the high-quality organization of current work, for example preparation of events, materials for public expertise reviews, results of public control, etc. At present, 44 regional budget laws have a separate line for ensuring the activities of the Civic Chamber. Each constituent entity decides on the issue of ensuring the activities of the civic chamber based on its capabilities; therefore, the level of financial support for the chambers' activities varies significantly: 8 chambers have financing exceeding 10 million rubles per year, another 10 have from 5 to 10 million rubles, and 20 have from 1 to 5 million rubles. The Budget Law of other constituent entities has no separate budget line for the activities of the Civic Chamber, and funds may be received from the budgets of regional ministries and departments, for example from a ministry of labor and social security. The perennial lack of funding for ongoing work significantly reduces the quality of work in public control, and independence in discussing various problems. The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation suggests that it is necessary to add a rule in regional legislation on the mandatory financing of the current activities of civic chambers.
Municipalities in many regions have created civic chambers. According to a survey conducted as part of the "Community" forum, nearly half of its participants already have experience of interacting with municipal civic chambers. The Moscow Region has civic chambers in all municipalities, and their activities are coordinated by the Civic Chamber of the Moscow Region. The Irkutsk Region has 14 municipal civic chambers (there are a total of 43 municipalities in the region). Some regions have such a network of public control at the local level.
At the final "Community" forum in Moscow, a scheme where operating both branch and rural public councils was introduced using the Ivanovo district of the Amur Region as an example. Out of a total population of 23,000 people in the district, more than 200 residents are members of various public councils.
At the same time, in a number of the Russian Federation's constituent entities there are no municipal civic chambers at all. Besides civic chambers and councils, many regions have other advisory bodies of social activists under the head of the region or mayor. And at the same time, the status of some public structures under regional authorities (councils on interacting with business entities and expert councils) is often not defined.
It is obvious that at the legislative level, the activities of municipal civic chambers are not sufficiently regulated. And in fact, they are only mentioned in the Federal law on public control. This situation creates an overlap regarding powers and jurisdiction of these institutions. The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation plans to launch an expert discussion on the legislative regulation of the activities of municipal civic chambers (councils).

#Public councils: new role in the work of authorities
Public councils are permanently acting consultative and advisory bodies of public control under federal executive bodies. The Public Council is intended to ensure that the needs and interests, and the rights and freedoms of citizens and public associations are protected and taken into account during the implementation of state policy, as well as to monitor the activities of federal bodies; for example, to consider bills, participate in monitoring of the quality of public services, evaluate the effectiveness of public procurement, etc.
According to the Federal Law “On the Foundations of Public Control in the Russian Federation”, public councils under federal executive bodies are formed on a competitive basis.27 In recent years the principles of autonomy and independence of public councils from public authorities have become a universally recognized norm. These criteria were developed with the participation of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, and were reflected in a resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation adopted in June 2019.28 The organizer of competitions to fill the vacancy in public councils is the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. The Civic Chamber establishes the basic requirements for candidates; candidates for the post of chairman of a public council are nominated by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. The term of office for the composition of public councils may not exceed 3 years from the day of the first in-person meeting of the composition of the public council.

Today, there are 51 public councils formed under federal executive bodies comprised of 1287 people. During the work of the current composition of the Civic Chamber (since June 2017), 31 public councils were formed, 18 of them work according to a new Activity Standard for public councils adopted in 2018. The submission of documents has been closed in 15 councils and the stage of verifying candidate profiles is currently underway. And also, since June 2017, 21 public councils have held competitions to replace outgoing members, and one previously formed council was totally “reset”.

Members of public councils discuss departments' current initiatives, consider socially significant bills, and supervise their implementation. They also monitor the quality of public services. Members of public councils have significant powers and expert competencies that allow them to influence the agenda of departments, and most importantly, they have the opportunity to know all the ropes of the department, without diving into the bureaucratic routine; and that is why councils can be quite useful for both government departments and civil society.
Such instances are out there. The Public Council under the Ministry of Natural Resources of Russia recorded the ineffective implementation of the federal target program “Lake Baikal Protection”. It is extremely difficult to implement the federal target program's key event - the elimination of the negative impact of waste accumulated by the Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill. In 2018, the Audit Chamber of the Russian Federation conducted an audit that showed an inefficient spending of funds, in particular, about 4 billion rubles were diverted from the budget, and spotted the non-execution of powers by responsible structures and the misallocation of funds. The Public Council under the Ministry of Natural Resources of Russia were provided with documents on the proposed changes in the federal target program to harmonize financial assistance to the region. Members of the Public Council as part of a Civic Chamber delegation visited the city of Baikalsk to assess the practicality of the amendments. Public activists were able to monitor the progress of the project to eliminate waste from the BPPM on the ground; the body implementing the project is "Rosgeologiya". During this event, it became clear that the start of the project had been delayed due to a lack of technological solutions. The Public Council gave specific proposals for changing this situation.30 In some instances, if the issue is related to a hyped up newsworthy event the media sparks lively discussions with the participation of media personalities. This was the case, when there was a discussion about a proposal by the Public Council under the Ministry of Natural Resources of Russia on the introduction of the subject “Ecology for Sustainable Development”. This topic was covered in 234 messages in the media, 2 clips on TV channels, and 726 messages on social networks.

Do you know about the activities of public councils under executive bodies in your region?
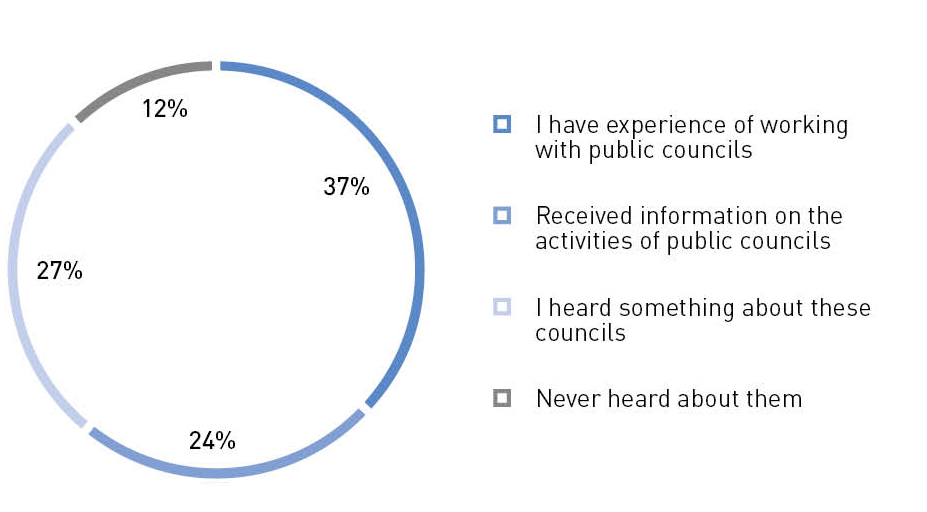
Source: The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation29

Such a proactive approach is inculcated slowly and is rather an exception than a tendency; today the potential of public councils is far from being fully realized. A public council can also discuss the organization's HR policy, including explicitly addressing the resignation of any official, but so far such precedents have yet to happen. Public councils often form an agenda based solely on institutional topics. There are public councils that are moderated by government officials. Often the councils are slow in reacting to social injustices appearing in the media, the legitimate claims of our citizens to the activities of state institutions, which has obvious consequences on the level of credibility and interest in them on the part of the population. Sometimes public councils have heated discussions, but their results remain unknown to the media and the public.
One of the most important tasks of public councils in the coming years will be to discuss and publicly monitor the implementation of national projects. Public councils shall become a platform for open and heated discussions on national projects: If there is any doubt that the stated goals will be completed on time, and the goals themselves need to be adjusted, this should be spoken about directly. This is an important format for civil society to participate in the implementation of national projects.
Regions, along with civic chambers, are forming public councils under executive bodies, and in some cases this is already a large-scale network of public control. Technically, this work involves tens of thousands of public activists throughout the country. Most respondents of a survey, conducted during the "Community" forums, already have experience in interacting with community councils in the regions or receive information about their activities.
In some state institutions, the activities of the capital and regional public councils are coordinated. For instance, members of public councils under the Federal Anti-Monopoly Service hold regular online meetings, as well as joint meetings in Moscow. In addition to interregional interaction assisted by public councils, interinstitutional interaction can also be organized. For this purpose, a Coordination Council under the Civic Chamber on the environmental safety of Russian citizens was created.

An interesting initiative to form an Assembly of regional public councils under relevant authorities was implemented by the Ministry of Construction of Russia. As a result an expanded public council that helps the federal institution receive feedback from the regions appeared.31 The first in-person meeting of the Assembly of Regional Public Councils in the areas of construction and housing and communal services were held in July 2019 at the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. The key topic of the meeting was the national project “Housing and Urban Environment” and the contribution of public councils to its implementation.
The dependence of public councils on regional authorities is gradually decreasing; the practice of appointing civil servants to public councils is almost history. For example, in 2014, the Civic Chamber of the Stavropol Territory monitored the civic councils of municipalities. At that time 62% of the councils were led by heads of administrations or municipalities or their deputies; the councils included state officials from various levels. Today, such tendencies have completely vanished.32
The activities of public councils in the regions are weakly structured and largely depend on the position of local authorities and their desire to hear the voice of civil society. To evaluate the contribution of these civil society institutions to the development of regions, solving local problems is quite difficult due to a few vivid examples of such councils' activities. The activities of public councils are regulated by regional legislation, which usually assigns them a role in the field of public control. If at the federal level the role of the Civic Chamber in the formation of the composition and coordination of the activities of public councils under federal executive bodies is clearly provided in normative acts, then the regions do not have such certainties. Some of the Russian Federation's constituent entities (Voronezh, Amur, Tambov, and Chelyabinsk Regions) have regional chambers that may participate in the formation of public councils.
In July 2019, the Kaliningrad Region adopted the Law "On Public Councils Under State Authorities". This legal act regulates the activities of public councils, the composition of which will now be in the hands of the Kaliningrad Region Civic Chamber, rather than of specialized ministries. Such a decision came from the local legislative body for the first time, and in some way it is an unexpected decision that creates a precedent, which could set an example for other regions.33 Moreover, the Kirov Region adopted amendments to the legislation, according to which the regional Civic Chamber forms 2/3 of public councils under regional executive authorities, coordinates the final composition of public councils that should provide the chamber with the results of their activities.
In some cases, the streamlining of the activities of public councils under regional executive bodies is carried out on an institutional basis. For instance, the system of public councils under the territorial bodies of the Federal Anti-Monopoly Service is conducted with the participation of regional civic chambers and with the coordinated support of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation.
Most laws in the regions still do not indicate powers of civic chambers to form public councils under territorial executive bodies. The participation of civic chambers in the composition of public councils is an important tool for ensuring the independence and productive work of these institutions. To resolve this issue, it is necessary to amend regional laws on public control, which enable regional civic chambers to participate in the formation of public councils.
#Civil society activists in the field of public control
The year 2019 marks five years since the entry into force of Federal Law No. 212-FZ “On the Basics of Public Control in the Russian Federation”. Despite the law clearly defining the structure of subjects of public control, the actual quality of its enforcement depends on the activity and competence of ordinary members in local public control, namely housing and environmental inspectors, members of civic chambers and councils, members of public monitoring commissions, leaders of non-profit organizations, etc.
Some regions of the country have a unified system of public control with clear rules of the game and the ability to quickly and effectively join in the work. For example, active public control was created in the housing and communal services system, initiated by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. Non-profit organizations served as a basis for creating resource centers for active housing owners, and the national project "Housing and Communal Services Control" is a methodological center for regional NPOs. Public inspectors monitor the activities of homeowners associations, the quality of capital repairs, and collect the opinion of residents about the quality of improvement of the outdoor space. A successful example is the experience of the Kirov Region where, since 2018, with the participation of the regional Civic Chamber, control has been established over the formation and approval of tariffs for housing and communal services. The final act, based on the results of complex monitoring of housing and communal service tariffs for 2018, it was noted that the requirements to limit the growth of tariffs has not been met and residents are paying an additional comparable amount through taxes.

At present, a system of public control around the implementation of the Law "On Immortalizing the Memory of the Fallen in the Defense of the Fatherland" is being developed. Today, according to the Russian Ministry of Defense, out of 31,078 military graves, the preservation level of 31% of graves has been rated as “unsatisfactory”. The maintenance of grave sites is managed by municipalities, which often lack the funds for this. The main activities in monitoring the status of monuments and grave sites are carried out by public organizations.34 The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, regional chambers, together with search NPOs, participated in the development of the federal target program “Creation and Restoration of Military Memorial Objects in 2019–2024”.35 The relevance of the program was confirmed by a public inspection of military grave sites in the Leninsky district of the Republic of Crimea and the city of Kerch, which did not always demonstrate a decent level of preservation and improvement, as well as the lack of passports for state registration of military grave sites in the “Memorial” unified database.

A monitoring system concerning orphanages is being developed to bring their activities in line with Decree No. 481 of the Government of the Russian Federation from May 24, 2014, which acts as the basis for reform in this sphere. According to data for 2018, the total number of individuals in orphanages is about 71,500 children. Almost 29,000 of them are children placed in these institutions by parents or other legal representatives. At the end of the last year, the number of orphanages reached more than 1,300, more than 90% of them are state-owned.36 The general task of the state and society is that a large number of children be brought up in families, preferably birth families. It is also necessary to reduce the time spent by children in orphanages, and stimulate orphanages to organize the family setting for their pupils.
The Civic Chamber also evaluates the provision of the services “Nannies for Orphans in Hospitals” according to Paragraph 88 of the action plan for the Decade of Childhood. It is necessary to improve the legal framework and expand the access of NPOs to the provision of social services to children.37
This year, after a visit by the President of the Russian Federation to the St. Petersburg Children's Hospice, budgetary federal and regional funding for palliative care for children was set. At the federal level, 4.6 billion rubles were allocated, and each region should add 20% to this money and create a regional development program for this sector. The Children's Rights Commissioner for the President of the Russian Federation, Anna Kuznetsova, together with the chairman of the Commission of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation Charity, Civic Education and Social Responsibility, Alexander Tkachenko, launched the monitoring of the organization of palliative care for children in the regions.38 On August 29, the first children's hospice was opened in the Moscow Region with the participation of Alexander Tkachenko in the city of Domodedovo.39
One of the most important forms of public control is an independent assessment of the quality of services provided by cultural, social care, health and educational organizations. According to Federal Law No. 392-FZ dated December 5, 2017, public councils for an independent assessment of the quality of social services were established under the Ministry of Culture of Russia, the Ministry of Health of Russia, the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia, the Ministry of Education of Russia, and the Ministry of Labor of Russia. These councils are formed by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation from representatives of all-Russian public organizations. They assess not the quality of services themselves, but the availability of conditions for their provision, i.e. openness and accessibility of information, comfortable conditions for the provision of social services, including waiting time, friendliness, politeness of employees at social care organizations, and accessibility of services for people with disabilities.
To date, the activities of these public councils are developing quite actively, but the involvement of contractors on public contracts who collect and summarize information about the quality of the conditions for the provision of services by organizations is facing problems. In light of this, it is necessary to consider the scope of powers of the Civic Chamber and civic chambers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation related to public councils for an independent assessment of the quality of social services, including participation in monitoring the results of the assessment and following measures on their results.

Since January 1, 2014, bills of acts of the Russian Federation's constituent entities concerning the implementation of entrepreneurial and investment activities must pass a mandatory procedure on the assessment of regulatory impact. The business community, empowered by the rights of entrepreneurs in the regions, is actively involved in this activity.
Since 2017, the Vologda Region has implemented the routine practice of conducting public control of road repairs. The region has allocated budgetary funds to launch a public control training program for municipal employees. The Kursk Region opened a free resource center for representatives of civil society and NPOs working in the field of public control, where they are provided with accounting and legal services for the whole year.
The development of a food quality control system is in process. The Komi Republic Civic Chamber, under the framework of the “Days of Control”, together with the Ministry of Agriculture and the consumer market of the republic, assesses the quality of dairy products.40 The project by Semyon Volchek, a contestant in the Civic Chamber “My Project is for My Country!”, “Interregional System for Monitoring the Safety and Quality of Food by Non-Profit Organizations as an Institution of Civil Society in the Field of Consumer Protection” operates in 20 regions. During the course of the project, they managed to significantly change the attitude of the public to the problem of counterfeit food products and its ingredients.
At the same time, many gaps remain in the sphere of legislative regulation and the organization of citizen participation in public control. According to the legislation, individual citizens and public associations are not subjects of public control, but they have the right to participate in its implementation. In order to do so they must have special knowledge and experience in the relevant field, as well as be officially approved as participants in public control (public inspectors, public experts, and public watchdogs). However, the procedure for empowering public inspectors, experts, and watchdogs are approved not in all areas of public control.
In light of this, the quality of sectoral laws in the field of public control should be improved. There are suggestions to provide subjects of public control with the procedural rights to apply to the court with a statement in protection of the interests of an indefinite number of people.
Today, the vast majority of regions have adopted laws on public control, but there are no laws on public control in the largest constituent entities of Russia, namely Moscow and St. Petersburg. The quality of regional laws varies widely: Some acts successfully detail and develop the norms of federal legislation, which makes the law a working instrument. The Kirov Region, the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District, and the Tyumen Region are good examples of laws on public control. In other cases, lawmakers simply reproduced the norms of the federal law.
A negative practice of public control exists, which has become widespread during inspections of business entities by public organizations according to Article 45 of the Federal Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights”, which, in particular, gives the right to conduct independent expert examination of goods, works and services, to carry out public monitoring of compliance with the law and, if violations are discovered, transmit this information to the competent authorities. Taking advantage of the legal illiteracy of business owners, dishonest employees of public organizations conduct raids among small and medium-sized businesses for personal gain. Similar violations exist in the system of public control in places of detention.
Additionally, legislation does not establish the responsibility of subjects of public control for distorted or inaccurate information, and the responsibility of persons who impede the implementation of public control. Further institutionalization of public control is necessary, including the requirements for the subjects of public control in the preparation and conduct of public inspections.
Examples of legislative regulation of citizen participation in public control

#Public Monitoring Committees (PMCs): humanitarian and social tasks
A special place in the system of public control is held by the institute of public monitoring commissions for public control to ensure human rights in places of detention (PMC).
The history of the existence of public monitoring commissions began in June 2008, when the law “On Public Control of Ensuring Human Rights in Places of Detention and on Assistance to People in Places of Detention” was adopted.41 Members of PMCs carry out inspections on a voluntary basis, outside their main working hours. The main purpose of control is to make sure that those who break the law are held in conditions that meet established requirements, and the rights guaranteed by the Constitution are strictly observed.
A feature of the activities of the PMCs in the Russian Federation is that, unlike other world analogues (“visitors” in the UK or France), members of a PMC in the Russian Federation are approved directly by one of the institutions of organized civil society – the Council of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. In this regard, the Council of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation bears a quite serious and painstaking work on the selection of candidates, requiring a responsible and balanced approach. Since the adoption of the law, public monitoring commissions in most regions have already replaced its their fourth composition of members. In total 367 compositions of PMCs members have been formed, 6,988 documents for candidates have been considered, of which 4,344 people have been appointed as members of PMCs. Sometimes there is criticism of the Chamber related to the fact that certain candidates were not supported. In this regard, it should be noted that the foundation of decisions is based on several criteria: the need for regular rotation of PMC members, the professional experience and reputation of candidates, and the quality of work of current members; the total score is based on the reports received by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation.

In 2019, the work of the Civic Chamber on the formation of new compositions for PMCs was distinguished by a special scale: 45 regions of Russia completed the procedure of forming new PMCs. As part of the campaign, 1,165 applications were submitted, of which 971 were recognized as complying with the requirements of the law. As a result of the competition, 709 people, or 60.8% of the total number of candidates, entered 45 PMCs. New PMCs were formed in the Nenets and Chukotka Autonomous Districts they could not be formed earlier, because there wasn't enough applications from candidates). The composition of PMCs have outstanding members: Well-known activists from the human rights movement, and professionals who are deeply involved in the topic.42 The maximum composition of the PMCs of 40 people was immediately formed in four constituent entities of the Russian Federation: Moscow, St. Petersburg, the Krasnodar Territory, and the Sverdlovsk Region. The number of PMCs members increased in another 17 regions where the rotation took place (in the Rostov Region, the Nizhny Novgorod Region, the Vladimir Region, the Komi Republic, etc.).
The Civic Chamber strives to attract as many active citizens as possible to work in the PMCs. The Civic Chamber prepared a guidance manual to help a candidate for the PMCs to understand the requirements of regulatory documents.43 The priority for the Civic Chamber is to increase the representation of candidates for PMCs from socially oriented NPOs, which could strengthen the work on social rehabilitation and social integration of prisoners. We should support the thesis expressed by public activists at the final "Community" forum that flawed members of society need support in difficult life situations and that they often have to start life over from scratch.
According to data obtained in consultations with the Presidential Grants Fund, in 2019, the Fund supported 42 projects in the sum of 91.1 million rubles in support of the rights of convicts and the work of PMCs. In 2018, 27 projects in the sum of 65 million rubles were supported. In 2017, 37 projects in the sum of 100 million rubles were supported. There are organizations that are subsidized by the Russian Ministry of Labor. But this is still not enough. The Civic Chamber will make every effort to facilitate the financing of the activities of non-profit organizations and foundations involved in the social reintegration of prisoners.
In 2019, as part of methodological support for PMC members, the members of the profile commission of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation conducted 15 events, carried out more than 30 visits to places of detention (mainly jointly with PMCs) in 19 constituent entities of the Russian Federation. A significant event for the participants in the human rights movement dealing with the problems of prisoners was the preparation of a special report by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation called “Ten Years of Activities of Public Monitoring Commissions in the Constituent Entities of the Russian Federation”.
Regular contact with the problematic agenda of public control in places of detention allows the Chamber to take an active role in improving the regulatory framework of PMCs activities. In 2018–2019, joint work with the Civic Chamber, allowed us to eliminate the following gaps in regulatory support and the organization activities: members of the PMCs were given the right to film, video, and photograph, measure temperature, humidity, and light in the places of detention facilities in order to record violations of the rights of detainees. The increase in transparency and the prevention of violations was facilitated by the withdrawal of medical service of the Federal Penal Service from direct subordination to the heads of institutions and territorial bodies of the penitentiary system; now they are directly subordinate to the Health Care Department of the Federal Penal Service of Russia.
Obviously, many issues in the activities of PMCs require further improvement both in terms of legislative support for their activities, and in terms of methodology. The level of work by commissions in different regions varies significantly. There is a big gap in the ratio of the number of members of PMCs and the number of places of detention in some regions. The legislation does not actually reflect the duty of the PMCs to report to the Civic Chamber: There is a norm that PMCs should send materials following the results of public control, however, neither the dates, nor the frequency of provision of these materials, nor their contents have been indicated. In light of this, the final "Community" forum demonstrated opinions on the need to strengthen feedback between the Council of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation and the existing members of the PMCs. In general, support was given to the idea that it would be reasonable to amend the legislation that clearly establishes the duty of the PMCs to regularly report on the results of its work.
A key problem is the material and technical and financial support of the PMCs activities. This is not about paying salaries to the PMCs' members, as they work on a voluntary basis, but about compensating them for the travel costs to the place of inspection, communication, the purchase of consumables, and other operating expenses: today, members of the PMCs pay their costs themselves. In some regions, places of detention are hundreds of kilometers away from the administrative center, which makes such trips very costly. In this regard, it is necessary to actively promote the issue of reimbursing the costs of implementing the PMCs activities from regional budgets.
Such a sensitive topic as the protection of the rights of prisoners, the highest requirements for transparency, and the ethics of public control must be respected. During the functioning of the PMCs, there are cases of abuse committed by their members; several former members of PMCs have been convicted of bribery. At the same time, the Civic Chamber today does not have legislatively fixed levers of influence on the activities of the already formed PMCs and their members; there is no procedure for removing members of the PMCs. In this regard, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation proposes to consider amending the legislation, which would provide the Council of the Civic Chamber with the right to remove members of the PMCs.
There is no doubt that the PMCs system has already made a significant contribution to improving the penal system in our country, and further progress in this area depends on our common efforts, perseverance, and adherence to the principle of civil society.
#Public expertise: contribution of the civil society to the quality of institutional environment
An important instrument of public control is public expertise. The task of public expertise is to hold a dialog and coordinate socially significant interests of various communities, authorities and business. The preliminary readings (“zero readings”) conducted by the Civic Chamber, actually give independent public assessment of the impact of the proposed decisions on the sphere of legislative regulation, the forecast of improvement or deterioration of the position of people, social groups, and conditions for entrepreneurial or public activities.
For 2019 (as of November 26, 2019), the Civic Chamber conducted expertise of 21 bills, of which 14 were in the format of preliminary readings, i.e. before the first reading in the State Duma.
The most important example of work in this area is the law on palliative care.44 The Civic Chamber held discussions in the regions. Meetings with experts from medicine and representatives of patient organizations, allowed to discuss the expanding of the concept of palliative care, the availability of pain relief, and various aspects of accompanying palliative patients at home. By the third reading, this legislative initiative passed a row of serious public discussions and to a greater degree reflected the opinion of the expert community and public organizations than the original version. In fact, it was public organizations that set the structure of the bill and the direction vector for state institutions. After the adoption of amendments to federal law, the concept of palliative care was expanded: in addition to medical services, palliative care should include socio-psychological and spiritual care.
In 2019, the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia developed a bill “On Amending Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation in Part of Improving the Regulation of the Activities of Socially-Oriented Non-Profit Organizations”, which provides for norms aimed at systematizing information on the provision by authorities of all levels of financial support to SO NPOs (socially-oriented non-profit organizations) through their listing in the Single portal of the budget system of the Russian Federation, improving the reporting system of NPOs, inspections cycle, provision of SO NPO individual state support measures established for small and medium-sized businesses with the same number of employees and the size of income, as well as special conditions for participation of SO NPOs in the privatization of the leased state and municipal property. According to the results of public expertise held by the Civic Chamber prepared a report containing commentaries and suggestions to the bill. In particular, it was noted practical problems that need to clarify the projected provisions to solve problems that facing SO NPOs during the formation and submission of reports to the Ministry of Justice of Russia.

Criticism was sparked by provisions establishing quantitative characteristics of the average number of employees (“from 101 to 250 people”) and income level (“from 800 thousand rubles to 2 billion rubles”) as a condition that will be taken into account when deciding on providing SO NPOs with support by organizations forming support infrastructure for small and medium-sized enterprises (borrowing, guarantees and sureties). Given this condition, new types of support will be able to use only large NPOs. At the same time, credit provisions and independent guarantees are being desperately sought by small NPOs that implement social projects (providing services in the social sphere) and do not have other stable sources of financing their activities.
As of November 25, 2019, the bill was not submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
The bill on non-stationary and retail delivery trade, which was also discussed as part of a public expertise at the site of the Civic Chamber, affects both the interests of business and consumer rights. In particular, it introduces uniform approaches and basic principles for registering the right to place non-stationary trading facilities and reflects such key points as the conclusion of contracts for retail trade for a period of five to seven years, a one-time extension of the contract without bidding, priority retail place and a number of other provisions. It is assumed that the municipal authorities will introduce amendments to the layout of objects of non-stationary trade for public discussions involving residents and business entities interested in placing these non-stationary or mobile retail facilities.45 Supporting the bill as a whole, the Chamber in its conclusion proposed a number of clarifications to balance the consumer’s safety and increase the mobility and accessibility of the distribution network.
The bill was submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on December 5, 2018. As of November 25, 2019, the date of consideration of the bill in the first reading was not determined.
Following the results of public hearings on a package of bills regulating taxi services, the Civic Chamber drew attention to the need for conceptual revision of the bill. Supporting the introduction of compulsory insurance of civil liability of transport operators, the Civic Chamber proposed to detail the responsibility of all market players (representatives of aggregators, taxi-booking services, authorized bodies, drivers), and develop and consolidate a detailed procedure for such liability.46
Bill No. 481004-7 was submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on June 5, 2018, and was adopted in first reading on December 13, 2018. The corresponding bill No. 428641-7 was sent to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on March 29, 2018, adopted on first reading on October 17, 2018. As of November 25, 2019, the date of consideration of both bills in the second reading was not determined.

The bill regulating the work of cultural professionals was harshly criticized by them regarding the introduction of regular (not more than once every three years) competitions to confirm the qualifications of cultural professionals with whom labor contracts were concluded for an indefinite period. An amendment to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides employers with the right to terminate a labor contract based on the results of a competition or if a cultural professional refuses to participate in it. The Civic Chamber suggests that the novation does not fully take into account the specifics of the work cultural professional, and the criteria for confirming qualifications do not indicate their professional skill and quality of work, but only come down to quantitative indicators.47
As of November 25, 2019, the bill was not submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
The discussion of the bill on “cyberdruzhina” (cybersquad) whipped up public talks. The bill prescribes the cooperation of volunteers who spot extremist information on the Internet with law enforcement agencies. It is assumed that cyberdruzhina will struggle with posting information prohibited in Russia on the Internet, including that aimed at promoting war, inciting ethnic, racial or religious hatred and hostility, as well as information which dissemination is punishable by criminal or administrative law. The main fears of those opposed to the bill are related to the censorship on the Internet, transformation of the new law into an instrument of pressure on freedom of speech and settling personal scores. And at the same time, the hearings in the Chamber had comments that the bill should regulate the existing practice of working with cyberdruzhina, including such controversial as, for example, provoking pedophiles.48
As of November 25, 2019, the bill was not submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
Of course, the teaching community supported amendments to the Law on Education, aimed at reducing the paper reporting of teachers. The bill, which was considered as part of the preliminary readings in the Civic Chamber, provided a limitation of the list of documents which pedagogical workers should prepare. Often, the administrations of a number of educational organizations shift their responsibility for the formation and maintenance of reporting onto the shoulders of teachers, which affects the quality of their basic duties.49
As of November 25, 2019, the bill was not submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
Participants of the hearings in the Civic Chamber pointed out significant shortcomings of the bill on the quality and safety of food products and amendments to article 37 of the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” (on school meals). In particular, it was pointed out that the basic terms of the law are not unambiguous and have loopholes.
For example, the term “healthy nutrition” does not take into account the age-related, physiological characteristics of the body, including mental and physical stress. The terms “food safety” and “unacceptable risk” have evaluative categories; “food products for baby nutrition” does not contain requirements for differentiation depending on the age and physiological characteristics of children; “hot meals” is defined as “a product that is brought to culinary readiness”, but it is clear that temperature and culinary readiness are not identical concepts.
Among the significant shortcomings of the bill, the participants of the hearings noted a too broad interpretation of the concept of “food product turnover”; the absence among 18 well-developed GOSTs for the organization of public catering a separate standard for the nutrition of children in pre-school, school and social children institutions; the inability to track down the monitoring of GMOs; the need to develop a GOST on the control of non-dairy fats and other components associated with dairy products; the blurring of the concept “authenticity of food products”.
Bill No. 797249-7 “On Amendments to the Federal Law 'On Quality and Safety of Food Products'” and article 37 of the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” regarding the improvement of legal regulation of the quality of food products” was adopted by the State Duma in the first reading. As of November 29, 2019, the date of consideration of the bill in the second reading was not determined.
Following a public expertise, a bill elaborated by the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia “On Amendments to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation Regarding the Establishment of the Specifics of Labor Regulation of Persons Working with Employers Who are Non-Profit Organizations” was supported. The bill is aimed at reducing the additional resource burden for NPOs on the development, approval and amendment of personnel documentation. For this purpose, the document provides NPOs with the features of labor regulations of employees working for small business entities, namely, it is proposed to establish the possibility of concluding, by agreement of the parties, a fixed-term labor contract by persons entering into work relations with NPOs, as well as the right of NPOs as employers to refuse local regulations containing labor norms.
As of November 25, 2019, the bill was not submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
The Civic Chamber supported the bill banning "booze shops" in residential buildings. Participants of the public expertise emphasized that the quality of life and the safety of citizens should be the highest priority of the state policy. Thus, the bill proposes to provide state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with the right to establish additional conditions for the retail of liquor in catering services in apartment buildings, including a complete ban on the retail of liquor products, based on a decision of the general meeting of premises owners in an apartment building made according to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. The bill also plans amendments aimed at establishing restrictions on the minimum area of the customer area (with a total space at least 20 square meters) and requirements for compliance with regional legislation on ensuring peace and quiet of citizens.
According to the participants of the public expertise, the changes proposed in the bill are aimed at eliminating the existing negative consequences and reducing social tension in the field of public relations under consideration. Moreover, participants of the public expertise suggested that the proposed restrictions in the bill extend to low-alcohol drinks as well.

The bill was submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on March 29, 2018, adopted in first reading on September 24, 2019. As of November 25, 2019, the date of consideration of the bill in the second reading was not determined.
A particular interest among the public and the professional community was sparked by the bill “On Amending Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation (Regarding the Ban on the Creation and Operation of Unitary Enterprises)”, elaborated by the Federal Antimonopoly Service in order to protect competition in local markets.

The Civic Chamber considers that the provisions of the bill do not take into account the consequences of the withdrawal of unitary enterprises working with socially significant markets (in which there are practically no private enterprises) and operating in underpopulated remote urban districts and settlements where competition is completely absent or at a very low level. In this case, this is the reference to socially significant areas of activity where daily maintenance of the proper level of ensuring the needs of the population is necessary in order to create comfortable living conditions for people. Among them, in particular, include transport services, removal of domestic waste and refuse, supply of utility services, cleaning of streets and roads, pharmacy, etc.
The liquidation of unitary enterprises in socially significant areas in the absence of legislative consolidation of alternative effective mechanisms for resolving vital issues for the population can lead to social tension and a deterioration in the quality of life. The discussions in the Chamber demonstrated opinions in favor of differentiated approach, taking into account the state of competition in socially important sectors in remote, inaccessible settlements, i.e. in areas with low investment attractiveness and low profitability. In addition to issues related to attracting business entities to work in those segments occupied by SUEs (state unitary enterprise) and MUEs (municipal unitary enterprise), there will be an acute problem of employing people released from these unitary enterprises. If a unitary enterprise is a city-forming enterprise, then its reorganization can have serious negative consequences for the territory.50
The bill was adopted in first reading on December 11, 2018. As of November 25, 2019, the date of consideration of the bill in the second reading was not determined.
The Civic Chamber considered simultaneously within the public expertise a bill banning the creation and implementation of unitary enterprises and a bill of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the Implementation of the Activities of State Unitary Enterprises” aimed at preserving certain types of unitary enterprises.
The Civic Chamber drew attention to the premature development of this bill prior to the adoption of the bill “On Amending Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation (regarding the ban on the creation and implementation of the activities of unitary enterprises)”, and at the same time formulated proposals for the refinement of the list of activities for the implementation of which state unitary enterprises can be created with activities aimed at ensuring socially significant functions such as, e.g. drinking water and food supply of settlements in remote and inaccessible areas; the activities of housing and communal services (communal services, operability of boiler houses, etc.); street and road maintenance services (outdoor space cleaning and watering, snow and ice removal, maintenance of the territory) and others.51
As of November 25, 2019, there was no information on the further progress of the bill.
Issues of immortalizing those who died defending the Motherland and improving the legislation in this area are under constant focus of the Civic Chamber. Thus, the Civic Chamber, as part of a public expertise, took an active part in the refinement of the bill “On Amending the Law of the Russian Federation 'On Immortalizing the Memory of the Victims in the Defense of the Motherland' (hereinafter referred to as “the bill, the draft of federal law”) and the draft order of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation 'On Establishing the Procedure for Interaction of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation with State Authorities of the Constituent Entities of the Russian Federation, Local Government and Public Organizations on the Issues of Immortalizing those Who Died During the Defense of the Motherland, the Procedure for Verifying the Information Contained in the Names of Persons who Died During the Defense of the Motherland, and Used When Inscribing Memorials and Objects, as well as the List of Information on Persons Died during the Defense of the Motherland Indicated on Memorials'”, proposing to expand the list of powers granted by the bill to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to immortalize those who died in the defense of the Motherland and the maintenance of military gravesites within their territories, as well as formulating proposals to detail the procedure for verifying the information contained in the name lists of those who died during the defense of the Motherland, and to make inscriptions (changes in them) on memorials.52
As of November 25, 2019, the bill was not submitted to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation. No further information on the progress of the bill.

The Civic Chamber annually holds a preliminary reading of the draft of the federal budget, and stands for the priorities of modernization of the social sphere and national development objectives reflected in this highly important financial document for the country. According to the participants of the hearings, while the state budget revenues are increasing (only this year they grew by 10–11%), the draft of the federal budget in 2019 includes an increase in expenditures only by 0.7% of GDP (up to 16.8% GDP), and in 2020 by 0.5% of GDP (up to 17.3% of GDP). At the same time, in 2019, citizens' incomes shrunk by 1.5%.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia, considers the document as balanced and verified. However, according to the members of the Civic Chamber, the project developers lack an understanding of the wide social context in which the Russian economy is immersed.
Among the main problems is the effectiveness of budget spending. An adoption of the budget at the end of the current year has become a common practice, and budgetary funds, are received no earlier than July – August, after the completion of all necessary procedures, in particular tenders for public procurement, and the work must be completed before the end of the year. The weak efficiency of the Law on Public Procurement (44-FZ) is due to the fact that tenders attract companies of a poor understanding of the subject area, and the main criterion remains the price of goods and work (services).
Participants once again noted the need for a wide expert discussion of the draft of the budget at an early stage, when considering its main conceptual provisions, macroeconomic forecast and key indicators.
Other legislative initiatives that were also discussed in the Civic Chamber include headline-making bills on the prevention of domestic violence, animal cruelty, distributed custody, requirements for the alcohol advertising, improvement of the state cadastral valuation, improvement legislative mechanisms governing children's access to cultural values and cultural goods, on enabling students' admission to educational activities and others.
At the regional level, an agenda of public expertise is formed around legislative initiatives that are of fundamental and strategic importance for the development of a particular region and the quality of life. For example, the Civic Chamber of the Stavropol Region held a discussion on a bill on Caucasian Mineral Waters elaborated by the Ministry of North Caucasus Affairs. The Chamber stated that the proposed initiatives lead to the emasculation of the legal status of a specially protected ecological-resort region of federal significance.53
As of November 25, 2019, the law was under consideration by the Council of Federation of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation. The conceptual proposals of the Civic Chamber were brushed off.
Based on the experience of conducting public expertise by the federal and regional civic chambers in 2019, it seems advisable to promote the following initiatives aimed at increasing attention to the institute of public expertise and its effectiveness:
- routinely recommend subjects of public control to use the “Official Website for Posting Information on the Drafting by Federal Executive Bodies Regulatory Acts and the Results of Their Public Discussion” (https://regulation.gov.ru) when conducting a public expertise of the regulatory acts;
- oblige responsible federal executive bodies to update timely information on public discussion of bills within the time period established by law, by posting the current editions of such regulatory acts on the “Official Website for Posting Information on the Drafting by Federal Executive Bodies Regulatory Acts and the Results of Their Public Discussion" (https://regulation.gov.ru);
- to amend the legislation which defines obligation of the subject of legislative initiative to send a reasonable response to the conclusions of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation and civic chambers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation based on the results of a public expertise of regulatory acts;
- oblige the federal executive authority developing a bill, to delegate their representatives to attend public hearings at the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation on the expertise of the regulatory act.
#Local and territorial self-governments as an environment for forming civic engagement
Local self-government is one of the key areas in the activities of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation in 2019. The Chamber stands for removing barriers and improving interaction between civil society in the regions, local self-government and regional authorities. This was addressed through a public expertise of the draft of the Federal Law No. 631751-7 “On Amendments to the Federal Law ‘On General Principles of the Organization of Local Self-Government in the Russian Federation’” regarding the improvement of issues of the territorial organization of local self-government.

The Civic Chamber formulated a number of proposals and comments, in particular, on the unlimited shift from a two-tier system of local self-government to a single-tier, which risks a concentration of municipal authorities at the "district" level and conflicts with constitutional norms (Chapter 8 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation) and the general concept of the Federal Law of October 6, 2003 No. 131-FZ “On General Principles of the Organization of Local Self-Government in the Russian Federation”.
As practice shows, it is necessary to make broader use of mediation mechanisms in public hearings, which would imply the participation of a reputable independent mediator in the dispute settlement process. During the "Community" forums, the idea of creating a unified electronic register of public hearings, the maintenance of which could be undertaken by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation repeatedly appeared.
The strategic goal is to reformat the institution of public hearings in a way allowing to create working groups of public representatives, public councils on urban planning and architecture issues under municipal administrations and under district administrations, which will be involved in projects at the earliest stages of planning any object, and to assign to public hearings a role of a real barrier through which one cannot drag any society-unfavorable decision.
To this end, in 2020, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation intends to analyze the regulatory legal sources governing public hearings during urban planning in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and prepare proposals for amending the legislation in order to implement the procedure for carrying out these procedures.
For example, it is necessary to involve residents of cities and villages in modeling the urban environment and developing the transport system of the regions. Today, there are many successful examples of the participation of civil society in the development of urban space; projects are often implemented in new interesting formats. Specifically, transport infrastructure and accessibility are the most important condition for the development of small cities. A key advantage is made up of the connection of the place both with the outside world and with the surrounding settlements. There are already successful practices where residents determine themselves buses' routes. An example is the city of Tutaev in the Yaroslavl Region, whose residents designed the city transport system with their own efforts.54
Great hopes are associated with the development of proactive budgeting, when the residents of the territories are directly involved in determining priority problems of local importance and the distribution of part of the budget funds, and in addition, connected to public control of the projects implementation.
The Komi Republic allocated 90 million rubles within the framework of the project "People’s Budget" to implement local initiatives, with a focus on improving settlements.55 In 2019, the Primorsky Territory, for the first time held a competition of projects initiated by groups of citizens, and TSGs (territorial self-governments). The winners among rural settlements received 100 thousand rubles, the winners from urban settlements 200 thousand rubles, and from urban districts 500 thousand rubles.56
The Bryansk Region allocated 100 million rubles for the implementation of 89 proactive budgeting projects.57 A discussion of the initiative “Interactive Budget for Citizens”58 which is underway at the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, allows residents to participate independently in the formation of the municipal budget and propose their initiatives to local authorities. In the future, this project could be a real breakthrough in the organization of local self-government in Russia. An important format for discussing and solving local problems is the territorial bodies of territorial self-government (TSGs), which were widely developed in some regions. In June 2019, the Civic Chamber held one of the "Community" forums, which cover the topic “Citizens' Self-Organization and Local Self-Government” in the Arkhangelsk Region, a region where TSGs have long and active experience of development. The TGSs movement provides serious support in solving local problems and allows reaching a qualitatively new level of territory development. Often TGSs implement completely extraordinary and unique initiatives and projects.

The Voronezh Region created about two thousand TGSs and launched a special regional grant program for TGSs. In Buryatia, the TGSs movement began to develop in 2010, and currently more than two thousand TGSs operates in the region, and since 2012, holds annual republican contest "The Best Territorial-Public Self-Government".59 The Bryansk Region has 605 TGSs, which address issues of improvement, fundraising for self-taxation, help with paperwork and are actually voluntary assistants to heads of rural settlements.60

Often, it is a territorial self-government that is the most understandable way of co-organization for people to solve specific problems. In many cases, territories are developing exactly where TGSs are created.
There are other interesting examples. In 2019, the Primorsky Territory for the first time held a projects competition initiated by residents of municipalities of the Primorsky Territory to resolve local issues. Projects could be submitted by initiative groups of citizens and TGSs.61 The Ulyanovsk Region holds the Festival of Local Communities, a platform for the "collection" of public initiatives to develop settlements, improve infrastructure, and mapping of problem fields and growth points on the territory of municipalities. The Civic Chamber of St. Petersburg supported the project "Open Petersburg", the main idea of which is to build credibility between the state and society. Interactive maps of St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region were presented on the developed website, where residents could choose the district and municipality, vote for a particular project and leave their comments. In total, over 8,000 responses, initiatives, and solutions to various problems were received. The contest helped to reveal objective results of the work of the city district administrations, which helped to establish a dialogue between society and the authorities.
A serious resource for the formation of an active civil society is the development of housing self-government. According to the Housing Code, owners of apartment buildings are responsible for the maintenance of common property, they are obliged to participate in general meetings and make decisions regarding the life of the house. Each house must have a Council of an apartment building (the only exception is the house in which the homeowner association is created). Housing activists groups and apartment building councils, working mostly for free, are the most massive volunteer detachment in this country, performing a huge amount of work.
Among the leading topics in the citizens’ petitions to the contact networks of public control in the field of housing and communal services are charging fees for housing and communal services and complaints against the management of apartment buildings and inappropriate management. A paradoxical situation takes place: The government keeps on adopting new regulations; licensing of homeowners association has been introduced, but the house management is downgrading. This is because the owners do not have mechanisms to control the situation.
Today, citizens play a passive role in the sphere of management of apartment building. As a rule, in practice, owners neither participate in meetings, nor make important decisions on house management, nor choose councils of apartment buildings, nor control the work of homeowners association. At the same time, instead of fulfilling their duties and exercising rights to manage the house, many prefer to solve problems by complaints to the supervisory or regulatory authorities. Such a paternalistic position is largely generated by the authorities themselves. Despite constant statements that the most important task is the formation of a class of active and responsible owners of apartment buildings (this task was particularly declared as a priority in the development strategy of the housing and communal services until 2020), specific decisions made by the authorities contribute to a decrease of owners activity. In particular, the role of general meetings in deciding the selection (re-election) of homeowners association was seriously reduced. Currently, to change management of an apartment building, changes to the register of licenses must be made first. In this case, from the moment of the meeting to the moment the record is changed, several years may pass, which makes the owners doubt that they can really control the situation in the apartment building.
The owners have no real advantage for the financial impact on the management organization. Regardless of the quality of work of this organization, owners' money continues to be credited to the organization's account. Often, owners are deprived of the opportunity to use and dispose of the common property of apartment buildings, which by law they own together. However, in fact, the common property of apartment buildings (attics, cellars, prams, and elevators) is alienated in favor of certain legal entities and individuals or transferred “to the balance sheet” of municipalities. The Civic Chamber is currently actively working to protect the rights of owners of common property and considers this direction one of the most desirable among citizens.
#Media environment and challenges of information society
The mass media is the most important institution of civil society, which is a feedback channel between citizens and the authorities, and it serves as an instrument of public control, and broadcasts common and shared semantic values that unite the society.
Surveys show that the mass media still has credibility of Russian citizens and holds third place in the rating of credibility after the army and the church.62 The information environment in this country has been developing very dynamically in recent years, and rather than based on the traditional mass media, but through an increase in the segment of electronic communications, and the development of the Runet. The Internet has already dramatically changed the structure of the information consumption of millions of Russians, and this trend will only increase.
And at the same time, the latter trend also carries certain dangers associated with the absence of any filtering system and verification of the information distributed on the network, which opens wide opportunities for misinformation and manipulation of public consciousness. Not less important matter is the general regulation of the Internet space. It is no secret that for public insults in the press a person may be brought before court. Meanwhile, the Internet space until recent times has remained out of any control. This problem is one of the most pressing; it attracts the attention of the state and the civil society and is constantly on the discussion agenda of the Civic Chamber.
On March 18, 2019, the Federal Law “On Introducing Amendments to the Federal Law “On Introducing Amendments to the Federal Law ‘On Information, Information Technologies and the Protection of Information’” was signed.63 This legislative act empowers the Prosecutor General of the Russian Federation and his deputy to identify websites on the Internet that contain information that offends human dignity and public morality, obvious disrespect for society, the state, official state symbols of the Russian Federation, and the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Upon detecting information, that offends the state or society, the prosecutor general or his deputies contact Roskomnadzor, which must ensure the removal or block of this web-resource. It is proposed to introduce administrative liability for such violations, i.e. fines from 30 to 100 thousand rubles. The Law defines the procedure for removing such information from the web.64
On March 29, the so-called fake news law came into force.65 It prohibits the publication of inaccurate socially significant information disseminated under the fall pretense of truthful messages if it threatens the life, health, and property of citizens or undermines public order or security. This law is supported by a fine of 30 thousand rubles to one and a half million rubles. The Civic Chamber believes that there is a need for a law that will oblige social networks to monitor independently illegal content on their websites.
On May 1, 2019, the President of Russia V.V. Putin signed the so-called Law on the Sovereign Internet.66 The essence of the innovations is that Internet providers have to transfer to the disposal of Roskomnadzor technical equipment, which, if the Russian Federation is disconnected from the World Wide Web, will manage the domestic segment of the Network.67 The law entered into force on November 1, 2019, and a number of its provisions will come into force only in 2021.

Recent years have been followed by a dynamic transformation of the mass media. Social networks as a source of news is used by 37% of Russians. At the same time, the main news distributors are generally foreign social networks such as Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube.68 Literally today the dominance of Western mass media in the Russian information space is an evident problem with elements of censorship and prohibitions. For example, this year Instagram owned by Facebook deleted the account of the TV channel "Arkhyz 24" from Karachay-Cherkessia, which had 100 thousand subscribers, without any explanation, and then the account of the TV company "Dagestan" was also deleted without explanation. Also, the Google administration, which owns the video hosting YouTube, blocked without explanation access to the publication channel "Ridus".

As known, according to the requirements of the law the day preceding the voting, political propaganda cannot be disseminated. Despite the timely notification of Google and Facebook about the day of silence, this did not work: On September 7 and 8, Facebook was spreading advertisements and political materials but the head of the social network shifted the responsibility on advertisers.
The inevitable conclusion that it is necessary to oblige foreign mass media structures (mass media and Internet companies) operating in the Russian market to register legal entities in the Russian Federation that will operate under Russian laws. In this case, they will be fully responsible for their actions, including financial responsibility.
Unfortunately, we have to admit that the Russian mass media focused on foreign audiences are facing increasing pressure. In August, RT was fined £200,000 by a British mass media regulator "Ofcom", for "failing to preserve due impartiality". In recent years, numerous violations against Russian journalists and Russian-language mass media in the Baltic countries have been recorded: Russian journalists were not allowed to attend a trial on the events of 1991; the Lithuanian company "Init" was fined €150 thousand for refusing to suspend the relay of the Russian TV channel "RTR Planet"; VGTRK correspondent Olga Kurlaeva was deported, then she was accused of “a threat to the national security”; with the same wording the editor-in-chief of "Sputnik Lithuania" Marat Kasem, was detained at the end of May, etc.69
Remarkably, that most Western countries have the legislation that severely limits a foreign influence on the national mass media environment.
In September, the Civic Chamber launched its public control working group on Internet. The key task of which will be to analyze Western practices of regulating the Internet, as well as to develop measures that will help to counter the monopolization of the web mass media. During the discussions in the Chamber and at the "Community" forum, various positions were expressed. Including that we need analogues of such Internet sites as YouTube or Wikipedia. We must engage in the development of our own IT platforms that will help guarantee a sovereign Internet and ensure the information security of society.
The Civic Chamber pays special attention to the development of social advertising. In 2019, the All-Russian Public Opinion Research Centre indicated new data on the attitude of Russians to social advertising in the media. 71% of Russians believe that social advertising is needed, 24% are of the opposite opinion. In general, 47% of citizens did not see social advertising over the past year, but 22% saw it, saw or heard, 21% do not remember. If respondents saw such advertizement, then it was devoted to compliance with traffic rules (7%), the anti-alcoholism (6%), healthy lifestyle (4%), according to the survey. As indicated in the survey, most often respondents saw or heard social advertising on TV (56%), on the street – 46%, on the Internet – 31%, in clinics, schools, and universities – 23%. Almost half of Russians (44%) believe that social advertising should primarily be against domestic violence, 42% – anti-drug, and 38% - anti-corruption, 34% are sure that such advertising should motivate responsible behavior on the roads, another 32% – anti-alcoholism.70
The Civic Chamber has a Coordinating Council on Social Advertising and Social Communications, whose activities are aimed at improving the quality and effectiveness of social advertising, and enabling services for its distribution. The number of references to SO NPOs in the mass media and social advertising has increased in recent years. However, the 5% quota for social advertising in the mass media established in part 3 of article 10 of the Federal Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ “On Advertising” is not met. And according to the Coordination Council for Social Advertising and Social Communications under the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, the real share of social advertising on federal channels does not exceed 2%. Non-profit organizations complain about non-transparent procedures used by the mass media, especially TV channels, when making decisions on the placement or non-placement of social advertising, as well as its payment status. To increase openness, understandability and transparency of making such decisions, the instructions of the President of the Russian Federation, and the active assistance of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Communications of Russia, allowed to create commissions on social advertising under the Public Television of Russia, CTC Media, holding "Krasnaya Zvezda" media, "Gazprom-Media Holding”, VGTRK holding, and Channel One. Information about the work of the commissions and their approaches to place social advertising is available on the websites of these media.

The following remaining problems can be noted: the legislation does not regulate the conditions for placing social advertising in the media, i.e. allowed both paid and free placement of social advertising. SO NPOs that do not have significant funds, and in some cases carry out activities mainly depending on the state support (subsidies, grants), in most cases do not have the ability to pay for the placement of social advertising.
There are frequent cases when the names of these organizations are not mentioned in the plots of TV channels indicating the work of various SO NPOs, or in the materials prepared with their participation, do not mention positions of employees out of concern that such mention in free advertising will be interpreted by regulation authorities as unlawful, especially when it comes to SO NPOs that provide services payable by citizens, or receive subsidies from the budget. There is a need for a more thorough regulation of this matter. 29 regions have measures to provide SO NPOs with preferential terms for advertising spaces owned by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The vast majority of municipalities have no transparent procedures for placing outdoor social advertising.71 These and other issues remain in the field of view of the Coordinating Council on Social Advertising and Social Communications.
